Discs store digitally encoded video and audio information in pits -- spiral grooves that run from the center of the disc to its edges. A laser reads the other side of these pits -- the bumps -- to play the movie or program that is stored on the DVD. The more data that is contained on a disc, the smaller and more closely packed the pits must be. The smaller the pits (and therefore the bE
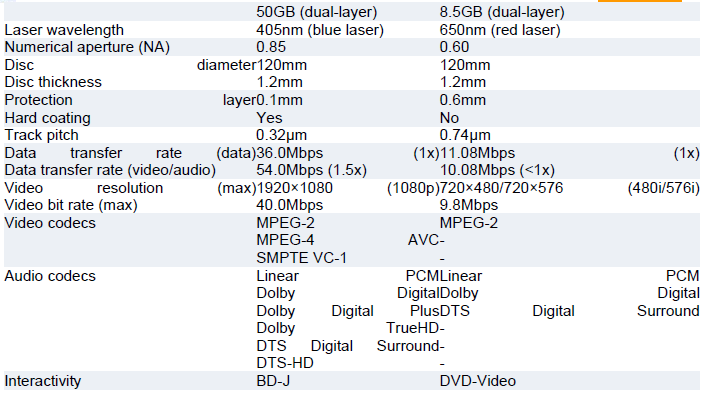
Unlike current DVDs, which use a red laser to read and write data, Blu-ray uses a blue laser (which is where the format gets its name). A blue laser has a shorter wavelength (405 nanometers) than a red laser (650 nanometers). The smaller beam focuses more precisely, enabling it to read information recorded in pits that are only 0.15 microns (µm) (1 micron = 10-6 meters) long -- this is more than twice as small as the pits on a DVD. Plus, Blu-ray has reduced the track pitch from 0.74 microns to 0.32 microns. The smaller pits, smaller beam and shorter track pitch together enable a single-layer Blu-ray disc to hold more than 25 GB of information -- about five times the a Each Blu-ray disc is about the same thickness (1.2 millimeters) as a DVD.
But the two types of discs store data differently. In a DVD, the data is sandwiched between two polycarbonate layers, each 0.6-mm thick. Having a polycarbonate layer on top of the data can cause a problem called birefringence sitting closer to the objective lens of the reading mechanism, the problem of disc tilt is virtually eliminated. Because the data is closer to th tect it from scratches and fingerprints. The design of the Blu-ray discs saves on manufacturing costs. Traditional DVDs are built by injection molding the two 0.6-mm discs between which the rec fringence. The two 2. The recording layer is added to o 3. The two discs are glued together. Blu-ray discs only do the injection-molding process on a single 1.1-mm disc, which reduces cost. That savings balances out th
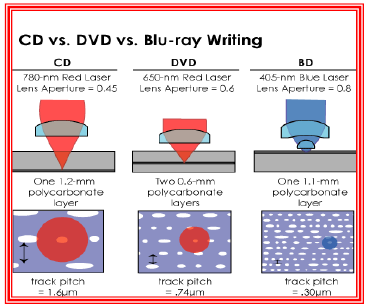
Blu-ray has a higher data transfer rate -- 36 Mbps (megabits per second) -- than today's DV Ds, whichtransfer at 10 Mbps. A Blu-ray disc can record 25 GB of materia
Formats
Unlike DVDs and CDs, which started with read-only formats and only later era different formats: • BD-ROM (read-only) - for pre-recorded content June 2006, the format had been available in the United States only for home recording, professional recording and data storage. In a press release dated June 15, 2006, Samsung Electronics America, Inc. announced the shipment of the industry's first Blu-ray disc player to retailers in the U.S. market. The Blu-ray disc players will be available for purchase on June 25th. (Sony's Blu-ray compatible VAIO VGN-AR190G PC is also y our new machine, Sony Pictures HoEntertainment is making some of its titles available i thF of Flying Dag 
|
|
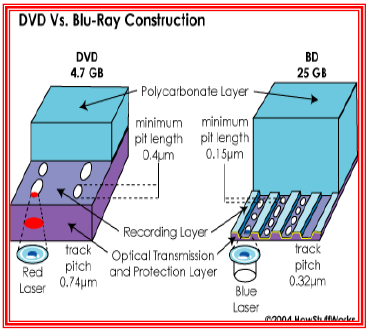
in which the substrate layer refracts the laser light into two separate beams. If the beam is split too widely, the disc cannot be read. Also, if the DVD surface is not exactly flat, and is therefore not exactly perpendicular to the beam, it can lead to a problem known as disc tilt, in ufacturing process. The Blu-ray disc overcomes DVD-reading issues by placing the data on top of a 1.1-mm-thick polycarbonate layer. Having the data on top prevents birefringence and therefore prevents readability problems. And, with the recording layer It seems that the future holds a whole lot more than 25 to 54 GB on a single disc. According to T3: DVDPioneer goes beyond sc that will blow away the hard disc in most of our PCs in terms storage capacity, holding 500 GB of data. How so? Pioneer's lasers are ultraviolet, which have an even shorter wavelength than the blue. There are also professional version blue laser technology. Sony has developed and ProData (Professional Disc for D ios. The latter is primarily for commercial data storage (for example, backing up servers).
When Will Blu-ray Become Available?
Blu-ray recorders have been available in Japan for some time, where more consumers have access to HDTV than in the United States. Outside of Japan, however, it has been a bit of a waiting game. Until price tag of around $3,000. The Samsung player hitting the U.S. market in June, the BD ent will be pri re rop as the format gains popularity. Even when the new video standard begins to replace current technologies, consumers won't have to throw away their DVDs, but they will need to invest in a new player. The industry is planning to market backward-compatible drives with both blue and red lasers, which will be able to play traditional DVDs an 00: The Samsung BD-P1000 plays Blu-ray software titles at the highest resolution available via a native 1080p HDMI output for films digitally mastered in 1920 x 1080p. The BD-P1000 also up-converts conventional DVDs to 1080p through the HDMI digital interface so the picture quality of any traditional DVD will look noticeably more detailed when used with the disc player. The BD-P1000 is backwards compatible and plays both standard DVDs and CDs in addit fo D Information collected: From Net and magazines. About the Author: Sri Shashwat Shriparv is MCA from ER & DCI IT, CDAC Ca |