Abstract
Agriculture which is the mainstay of Bihar economy suffers from drought and floods. Almost one-sixth of the total flood-affected areas of the country is in Bihar engulfing as high as 69 lakh hectares under it grip. Flood bring widespread damage to life and property, particularly to the weaker sections of society. In the presenario, the subject of interlinking of rivers is a matter of interest which is seen as a measure for sustainable control over water resources. This paper will focus on conceptual issues relating to RLP (River Linking Project) as well it identifies and enumerates the possible impacts on the nature and extent of some of these impacts.
Keywords: River Linking Project, Flood 
Introduction
Agriculture is the mainstay of Bihar economy which suffers severely from drought and floods. Almost onesixth of the total flood-affected areas of the country is in Bihar engulfing as high as 69 lakh hectares under it grip. Flood bring widespread damage to life and property, particularly to the weaker sections of society. In this paradoxial situation, suggestions for the transfer of water from surplus areas to deflict areas. Earlier Proposals, Dr. K. L. Rao’s - National Water Grid, 1972 and Dr. D. J. Daster’s - Garland Canals, 1977 but, these proposal were not found feasible and dropped. River Linking Project (RLP) identifies and enumerates the possible impacts on the nature and extent of some of these impacts.
Materials and Method
In this investigation the parameter considered may be as follows: - Judging the slope of the land because the river flows according to the gravity of slope. The source region of the basin from where they originate and aerial extent of the source region. The quantity of water found in the rivers. Agricultural development survey before XIth plan period and after XIth plan period. Differences in rearing fishes as fish catch in the river. The process of •Rajasthan-Sabarmati
•Chunar-Son-Baraj
•Son-Dam-Associates River of Southern Ganga
•Ganga-Damodar-Suwarnrekha
•Suwarnrekha-Mahanadi
•Kosi-Mechi
•Farakka-Sunderwan
•Jogigopa-Tista-Farkka
The peninsular Component
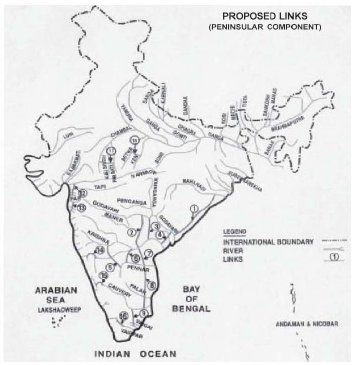
•Mahanadi-Godawari
•Godawari-Krishna
•Krishna-Pennar
•Pennar-Kawaeri
•Kaweri-Wegai-Gundar
•Ken-Betwa
•Parwati-Kalisindh-Chambal
•Par-Tapti-Narmda
•Daman Ganga- Pinjal
•Bedti-Warda
•Natrawti-Hemwati
•Pamba-Achankowil-Weipar
The RLP will involve large scale intervention in the natural hydrological system of the country. Implementation of RLP will require construction of large dams, barrages, distribution systems including cross-drainage works, to store water at strategic points and to distribute it to the farthest points to harmonize the spatial and temporal demand-supply disparity. Apart from the impacts on the social and economic aspects of the country. Most of these impacts are interactive in nature i.e., change in one aspect will As a consequence, serious drainage congestion is bound to happen in the upstream side of the channel banks inspite of construction expensive cross – drainage works.
Change in Ground Water Table (GWT):
Due to introduction of dam reservoirs and long large channels, the GWT will rise. It proves to be an asset for the dry and parched land in Bankura district, where the emergence of the reservoir and the canals implemented in the Kangsabati reservoir Project brought in more water during summer in the wells and tanks. here may be some adverse effects also due to GWT like water logging of agricultural lands in some area.
Impact Due to Lower Flows in Existing Rivers and Channels on River Regime, Water Equality and Ecology:
Lower flows have a baneful effect on the downstream reach of the river. This may affect morphology of the channel, aquatic biota, induce ingress of salinity in coastal regions Lower flows limit the capacity to reduce pollution through dilution. 21. Larger flows overflowing river banks, help in |
|
navigation and its usability in the area for socio economic development. Measurement of the process of alluviation and diluviation. Measurement of the area and amount of silt deposit
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
River Linking Project (RLP) is initiated on 25th August, 2005 namely “Amrit Kranti” which is most awaited project since 1972. National Water Development Agency As a result, the National Water Development Agency (NWDA), was set up in 1982 by the GOI under the ministry of Water Resources as an Autonomous Society to study the feasibility of the national perspective as formulated by the Ministry of Irrigation. The NWDA has come up with a proposal after some studies.
The proposals consists of two components viz.,
–The Himalayan Component -The peninsular Component The Himalayan Component
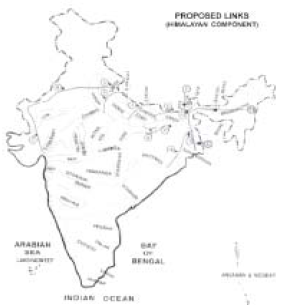
•Manas-Sankosh-Tista-Ganga
•Kosi-Ghaghra
•Gandak—Ganga
•Ghaghra-Yamuna
•Sharda-Yamuna
•Yamuna-Rajasthan
bring about changes in other aspects as well.
Impact on the Environment
•Rehabilitation of the project affected persons
•Sedimentation of Reservoirs
•Waterlogging of agricultural land
•Submergence of mineral deposits and archaeological
monuments/shrines •Aquatic life
•Submergence of rare species of flora and fauna
•Health impact
•Water quality
•Impact on Climate
Impact on the Environment
•Reservoir Induced Seismicity (RIS)
•Environmental Impact during construction
•Obstruction to cross country drainage due to
excavation of large link channels across the general slope of the country
•Eutrophication in reservoirs
•Change in ground water table
•Impact on society and wild life due to introduction of
canals cutting across social communication as well as wild life movement path •Reduction in flow in lower riparian part of the basin
•Terrain Capability
Reservoir Induced Seismicity (RIS):
The disastrous earthquake at Koyna reservoir, Maharastra and the failure of the Vaiont dam in Italy (Loss of 2600 human lives) put a big question mark on the question whether earthquake can be induced by the filling of a reservoir. These conditions arises when the existing rock strata arrangement is earthquake prone and additional pressure due to filling of reservoir may trigger off a strong earthquake. Environmental Impact During Construction:
Following factors may put adverse effects on Flora and Fauna of the forest land:- 1. Movement of heavy earth moving machinery.
2. Presence of a large number of workers.
3. Blasting of rock strata etc. Pollutions from automobiles, including noise pollution disturb the living condition of the wild animals. Obstruction to Cross-country Drainage due to excavation of Large Link Channels across the General Slope of the Country:
These link channels are likely to be aligned along the general slope of the country.
building up the flood plains, adding nutrient laden sediments, cleaning up the area, providing fish spawns These spawns add to the culinary delight of the people devours the mosquito larva restricts propagation of Malaria and other mosquito borne diseases.
Conclusions
The anticipated issues in all aspects should be identified and properly articulated. Detailed plans should be made public and a national debate should be initiated. In view of the water crisis looming large in certain areas and considering that economics of water will undergo radical change in the coming years it is surmised that the concept of inter-basin transfer cannot be summarily rejected. Any intervention which is likely to affect the trans-boundary co-basin countries adversely has to be sorted out and a satisfactory agreement reached well ahead of implementation.
References:
• Dr. K. L. Rao’s - National Water Grid, 1972.
• Dr. D. J. Daster’s - Garland Canals, 1977.
|