Route Simulator
Saumya Priyadarshini; Akanksha Anand; Abhimanyu Kumar
(Department Of Computer Science & Engineering)
R.P.S.I.T. Patna
| It is very difficult to decide a suitable path over which you can travel from one place to another under optimal cost (minimum traveling cost, through minimum distance, minimum time taken).There are many solutions available to solve this type of problem, like using road map, Internet surfing, or any other latest modern technique etc. But all of these are feasible on large geographical area, or these are beyond the reach of the common man .Similar situations come in our daily life when one wants to go to a desired place under a small geographical |
|
area , e.g. within a state or within entire city and he is a new person for that city as one may not be familiar to the sub-destinations coming under the path , the traffic rules of that particular area and any new disturbance in that path (may be due to construction work or other natural calamity) .These situations make traveler confused . To overcome this problem, we have designed a software based device; named “ROUTE SIMULATOR’’. Its virtual image is shown below: |
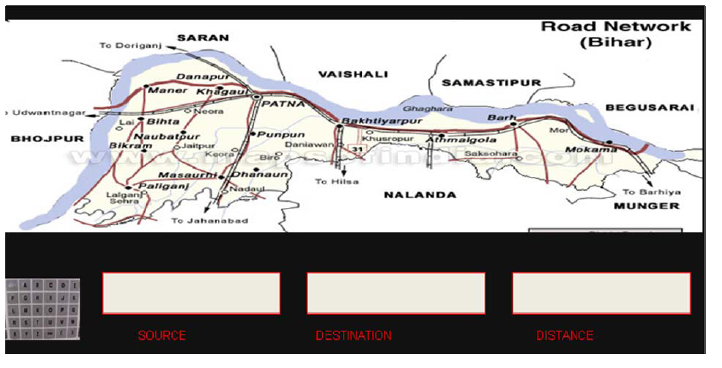
The device consists of a keypad through which inputs are feeded. This device takes two inputs from the end user ,that is source & destination ; and provides two outputs : one of these is distance and next and the most important one is the representation of shortest path including all subdestination on the display. This device is having map based information of the geographical area(city/state /as required ) in the form of weighted graph. Internally ,each place is represented as a node and distance between the two places is taken as edge of the graph. The software on which this device works is based on “Djikstra’s Algorithm”. It is a very popular and common purpose algorithm provided with Graph data structure .The algorithm is as follows :
The algorithm typically relies on the property that a shortest path between the vertices contains other shortest paths within it. For example , graph before and after processing algorithm are as follows: [Here the vertex ‘A’ is source and all others are treated as destinations].
Initial :
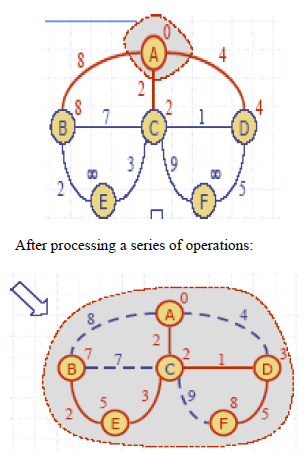 |
|
 The representation of screen by highlighting the shortest path is managed by “graphics under ‘c’ language.” The representation of screen by highlighting the shortest path is managed by “graphics under ‘c’ language.”
There are many advantages of this device which make it more feasible for common people :
• It follow the traffic rules.
• It is a perfect guide .
• Gives current updates of a path.
• It is quit reliable.
To make this device reachable to the common man , we have planned that it should be implemented as “Display Devices” on the public places like Bus stop, Railway station, front of Tourist center or government buildings etc. This can also be used in the inquiry office so that the people can have online help about the routes. Current updating due to any disturbances can be managed by route department government (e.g. PWD Dpt.) by setting the ‘weight’ of that path to ‘infinite’ in the ‘graph’. This device doesn’t work on any radar or satellite concept, so it is not very expensive and is reliable too.
|
|